Ballpark estimate: $15,000 to $90,000
The current job market for ultrasound technicians (also know as diagnostic medical sonographers) in the United States is strong, thanks in part to changes brought about by healthcare reform and also by the needs of an aging population.
As a result, the healthcare field requires a strong pool of highly trained professionals who are adept at using sophisticated electronic equipment and who understand the anatomy and physiology of the human body. If this sounds appealing, just in mind the training requirements to become an ultrasound technician are rigorous and expensive. In addition, working in healthcare attracts a competitive cadre of students to the best programs available, so you’ll need to put your best foot forward to be accepted into a good program.
Uses for Ultrasound Technology
Ultrasound technology has long been associated with prenatal care, providing doctors with a way to follow a woman who is expecting a baby in order to assess the health and development of the fetus throughout the pregnancy. While this continues to be an important use of ultrasound imaging, the process is now used as a diagnostic tool for many other medical conditions in adults and children as well.
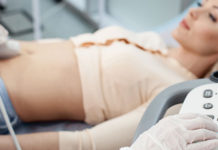
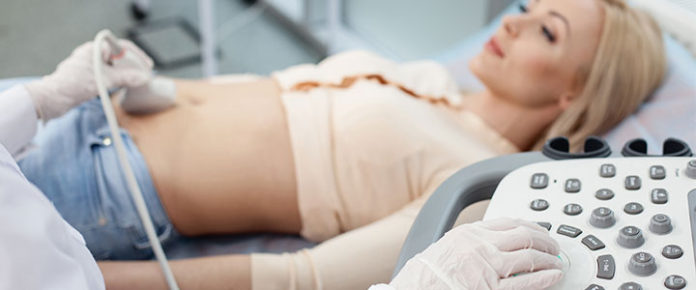
Diagnostic medical sonography uses high-frequency sound waves to create a detailed picture inside a patient’s body, reducing the need for invasive procedures and improving the information available to doctors when making a diagnosis. Sonographers often specialize in a specific area or system within the body, such as the abdomen, reproductive system, vascular system or the heart (echo-cardiogram).
Training Matters
In order to be hired as an ultrasound technician, you’ll need to complete a specialized training program. Depending on your current status and other career goals, you may select a certificate, an associate’s degree, or a bachelor’s degree. Someone who’s just heading to college from high school may want to consider spending the time to get a bachelor’s degree, while someone who already has a bachelor’s degree and has been working in a health-related field may opt for the quicker certificate program.
Whatever path you choose to follow, be sure to find a school that is accredited by the Commission on Accreditation for Allied Health Education Programs (CAAHEP). The majority of programs are accredited and this is an important distinction because prospective employers will want to know that you are properly trained. Before working in the field, graduates must also go on to become certified by the American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography (ARDMS). Certification requires both proof of formal education plus passing exams administered by ARDMS for general sonography and a specialty. While it’s possible to get certified after graduating from a non-accredited program, you may need work experience to qualify. This is a Catch-22 since it’s difficult to get hired without being certified first! That’s why it’s best to select an accredited program and avoid this dilemma in the first place. Continued education to keep up with the latest trends in the industry is also required to maintain current certification from ARDMS.
What to Expect
Diagnostic medical sonography programs often provide training in anatomy and physiology and physics (some programs require this coursework in advance) along with specialized training in how to operate and maintain ultrasound equipment. Interacting with patients is another important aspect of a good DMS program and is often taught through internships or clinical assignments before graduation.
Shopping Around for Programs
Before you decide on a school, do your homework. Find out about the specific curriculum by visiting the school’s website for a list of courses you will be required to take in order to graduate or receive your certificate. Some programs (particularly the certificate programs) will focus heavily on training students in a clinical setting, meaning they offer a hands-on style of teaching and learning. Other programs, such as an associate’s or bachelor’s degree, will require students to take general education requirements such as math, science, and electives in addition to their more specialized coursework so they get a complete education.
How to Find
One website that can help as you explore your school options is allalliedhealthschools.com, where you can search using multiple criteria. You can also check the Joint Review Committee on Education in Diagnostic Medical Sonography and the Commission on Accreditation of Allied Health Education Programs.
Cost to Become an Ultrasound Technician
As you look at cost for different programs of study, keep several factors in mind. Length of the program is often critical when considering cost. For example, a two-year certificate program from Loma Linda University in California will cost about $40,000. On the other hand, you can get an associate’s degree from Middlesex Community College in Massachusetts for about $15,000 and it will take about the same amount of time. Neither option includes the cost of room and board, which can add another $10,000 per year to the cost of attendance.
Obtaining a bachelor’s degree will typically take between three and four years and will cost significantly more than the other options. For example, a four-year bachelor’s degree from Loma Linda University will cost about $90,000 compared to $40,000 for the certificate program.
Adding It Up
Before choosing a school or program, it is also important to look at potential employers to see what they expect from applicants for ultrasound technician jobs. If most of your desired employers require a bachelor’s degree, you may want to explore ways that you can achieve that standard at a reasonable cost. For example, if you earn an associate’s degree from Middlesex Community College in MDS, you can transfer to one of the state universities in Massachusetts to complete a bachelor’s degree without losing any credits. Tuition for the final two years at University of Massachusetts Lowell, will cost about $23,000. This is a total cost of about $38,000 for a bachelor’s degree along with complete training in DMS. Not to mention the possibility that you may be able to secure part time work in the field while you complete your bachelor’s degree requirements. A similar type of educational path may be available in other states. Another option is Armstrong Atlantic State University in Savannah, Georgia. Their radiology bachelor’s degree has sonography as a choice within the broader program. Tuition costs about $7,000 per year for residents of Georgia (or $28,000 for four years) and about $20,000 per year for out-of-state students (or $80,000 for four years). Again, these prices do not include room and board.
Financial Aid
Financial Aid is an important consideration as you compare prices and decide on a program that’s right for you. This should be explored carefully with individual schools because each will have its own financial aid options. Be sure to carefully explore what type of scholarships and loans for which you might qualify before you make any decisions. You may be pleasantly surprised to find that some schools will offer financial aid packages that will make the cost for your attendance far more affordable than you originally thought.